Global China Unit
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesAs the world races to cut carbon emissions in the fight against climate change, a potentially game-changing milestone may have been reached.
China – currently responsible for some 30% of global emissions – saw its emissions decline in the 12 months up to May 2025.
Crucially, this would be the first time emissions have fallen even as demand for power across the Chinese economy grew rapidly. Previous drops have only ever taken place during shocks like the Covid pandemic, which slowed the country’s economy.
Given the outsized role the country – home to more than a billion people – has played in increasing global emissions in recent years, it is a moment to celebrate.
“The world would have stabilised its emissions 10 years ago if it weren’t for China,” Lauri Myllyvirta, of the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, points out to the BBC.
Mr Myllyvirta’s own research found China’s emissions were down 1.6% compared to the same period last year.
The need for China, and all countries, to reduce emissions has never been more pressing.
According to the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the world cannot simply stabilise the amount of emissions pumped into the atmosphere annually, if it is to hold global warming to below 1.5C. Warming above this temperature would lead to devastating effects for people around the world.
Instead, global annual emissions must start falling if the worst effects of climate change are to be averted.
So how has China achieved this?
And is this the first step towards a sustained decline, or a blip in China’s output?
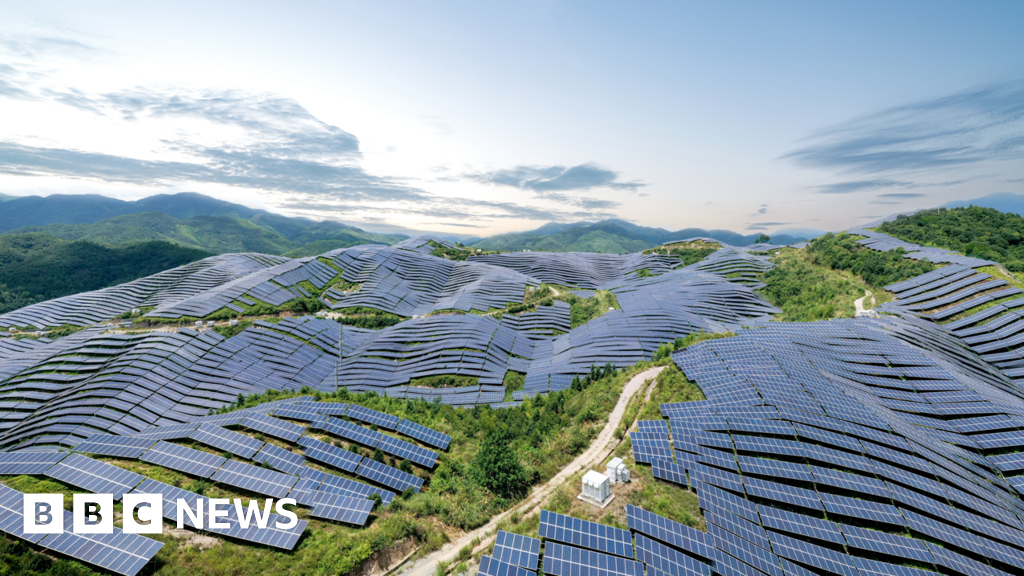
China’s green tech boom is helping…
Much of the decrease in emissions can be put down to countrywide investments in wind and solar.
According to Myllyvirta, China has installed more than half of the solar and wind generation capacity that has been installed globally over the past few years.
“The solar capacity that China installed last year is comparable to what the EU has overall,” he said. “It’s a staggering pace of growth.”
Recent data from the UK-based energy think tank, Ember, shows that in April, wind and solar energy together generated more than a quarter of China’s electricity for the first time.
Meanwhile, electricity generated from fossil fuels over the first four months of 2025 fell by 3.6% as compared with the same period last year.
These are dramatic changes for an economy historically dependent on coal, says Ember energy analyst Yang Biqing.
Yang adds that coal will likely remain important for some time, given that renewable sources on their own don’t provide a constant, stable supply of electricity.
China is not just installing these renewable energy technologies, but manufacturing them as well.
Chinese companies currently lead the world in making green tech, including wind turbines and solar panels – accounting for some 60% and 80% of global output, respectively.
These companies and their global competitors are now engaged in a rush for transition minerals across the world.
The industries’ rapid expansion – with their need for mines and processing plants – have caused severe social and environmental damage in the areas where they are located.
Recent findings by the Business and Human Rights Resource Centre, a non-profit, showed that the rush to mine these minerals was also fuelling human rights abuses and environmental destruction.
Nonetheless, the experts interviewed by the BBC agreed that China’s ability to deploy these technologies at scale had a decisive impact on levelling off its carbon emissions.
… but it’s not an outlier in fighting climate change
China may be installing renewables at a record pace, but its energy mix is still comparable with many Western economies.
In the UK, for example, renewables accounted for 46.3% of all energy generated. The US – second to China in carbon emissions – generates just over 20% of its energy from renewables.
Many of these developed economies, once leading emitters, also started reducing their emissions long ago, shifting away from coal and energy-intensive manufacturing.
China has long argued that it was only following the trail blazed by those wealthier countries, whose economic rise was accompanied by surging emissions. India’s emissions have also soared in recent years as it got richer.
Average emissions per person in both China and India are far lower than in the US – though China’s per capita emissions now exceed those of the UK and EU and are about the same as those of Japan.
So what’s next for China’s emissions?
They may have flattened out recently, but that does not guarantee a sustained drop.
“You could plateau at that level for a long time, and that’s not a very helpful thing for climate action,” says Li Shuo, of the Asia Society Policy Institute (ASPI).
Mr Li warns that turmoil outside of China’s borders could push Beijing back towards coal – the Ukraine war, for instance, fuelled Chinese leaders’ determination to secure energy supplies.
But the drive for energy security may actually push them towards renewables, says Christoph Nedopil Wang, director of the Griffith Asia Institute in Australia.
The way he sees it, the country’s “dominance” in the sector means relying more on renewables, and less on energy imports, only “improves national security for China”.
Current trade tensions with the West, and China’s sluggish economy, are also unlikely to prompt Beijing to stimulate its economy in ways that would lead to a renewed surge in carbon emissions, Dr Nedopil Wang adds.
Policymakers are placing bets on low-emission sectors, like IT, biotech, electric vehicles and clean energy technologies, and these are more likely to grow, he predicts.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesBut China still has a way to go in meeting its key international climate commitment.
Under the Paris Agreement framework, China has committed to reduce its carbon intensity by more than 65% from 2005 levels, with a deadline of 2030. Carbon intensity measures the amount of carbon emitted per unit of GDP.
In order to achieve this long-term goal, China set itself an interim target of cutting carbon intensity by 18% between 2020 and 2025. However, its efforts went off-track during the Covid-19 pandemic, and it had achieved only a 7.9% reduction by the end of 2024.
As a result, China’s only hope of meeting the 2030 target is to reduce emissions in absolute terms between now and 2030, Mr Myllyvirta says. The reduction he has identified is a start, he adds, but ambitious goal-setting and policy must follow.
Beijing may also start playing a more proactive role in global climate policy, Dr Nedopil Wang says: “That would be a big shift from 10 years ago, even six years ago, when China’s position was very much that ‘We’re a developing country and we hold back’.”
Such a shift is more likely now, as Beijing looks to take advantage of the Trump administration’s hostility to climate action to establish itself as a leader on the issue.
At a climate conference in April, President Xi Jinping told world leaders: “Instead of talking the talk, we must walk the walk… we must turn our goals into tangible results.”