BBC environment correspondent
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesA ground-breaking project to suck carbon out of the sea has started operating on England’s south coast.
The small pilot scheme, known as SeaCURE, is funded by the UK government as part of its search for technologies that fight climate change.
There’s broad consensus among climate scientists that the overwhelming priority is to cut greenhouse gas emissions, the chief cause of global warming.
But many scientists also believe that part of the solution will have to involve capturing some of the gases that have already been released.

These projects, known as carbon capture, usually focus either on capturing emissions at source or pulling them from the air.
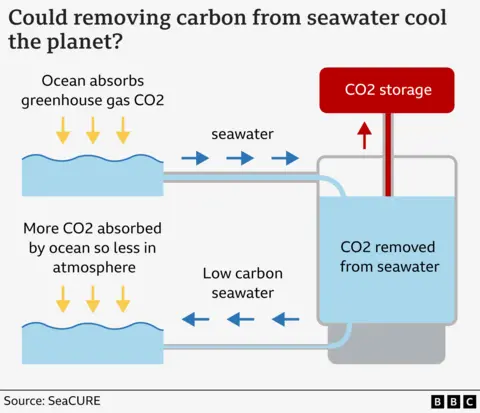
What makes SeaCure interesting is that it is testing whether it might be more efficient to pull planet-warming carbon from the sea, since it is present in greater concentrations in water than in the air.

To reach the project’s entrance you have to go round the back of the Weymouth Sealife Centre and walk past a sign that says “Caution: Moray Eels may Bite”.
There’s a reason this ground-breaking project has been placed here.
It’s a pipe that snakes under the stony beach and out into the English Channel, sucking up seawater and bringing it onshore.
The project is trying to find whether removing carbon from the water might be a cost effective way of reducing the amount of the climate warming gas CO2 in the atmosphere.
SeaCURE processes the seawater to remove the carbon before pumping it back out to sea where it absorbs more CO2.
We’re the first broadcast journalists to visit and Professor Tom Bell from Plymouth Marine Laboratory is tasked with showing us around.
He explains that the process begins by treating some of the seawater to make it more acidic. This encourages the carbon that’s dissolved in the seawater to turn into a gas and be released into the atmosphere as CO2.
“This is the seawater stripper” Prof Bell says with a smile as we turn a corner.
The “stripper” is a large stainless steel tank which maximises the amount of contact between the acidic seawater and the air.
“When you open a fizzy drink it froths, that’s the CO2 coming out.” Prof Bell says. “What we’re doing by spreading the seawater on a large surface area. It’s a bit like pouring a drink on the floor and allowing the CO2 to come out of the seawater really quickly.”
The CO2 that emerges into the air is sucked away and then concentrated using charred coconut husks ready to be stored.
The low-carbon seawater then has alkali added to it – to neutralise the acid that was added – and is then pumped back out into a stream that flows into the sea.
Once back in the sea it immediately starts to absorb more CO2 from the atmosphere contributing in a very small way to reducing greenhouse gases.

There are already much more developed carbon capture technologies which take carbon directly out of the air – but Dr Paul Halloran who leads the SeaCURE project tells me that using water instead has its advantages.
“Seawater has got loads of carbon in it compared to the air, about 150 times more,” says Dr Halloran.
“But it has got different challenges, the energy requirements to generate the products that we require to do this from seawater are huge.”
At present the amount of CO2 this pilot project is removing is tiny – at most 100 metric tonnes per year – that’s less CO2 than a commercial plane emits crossing the Atlantic. But given the size of the world’s oceans those behind SeaCURE think it has potential.
In its submission to the UK government SeaCURE said the technology had the potential to be massively scaled up to remove 14 billion tonnes of CO2 a year if 1% of the world’s seawater on the ocean’s surface was processed.
For that to be plausible the entire process for stripping the carbon – would have to be powered by renewable energy. Possibly by solar panels in a floating installation at sea.
“Carbon removal is necessary. If you want to reach net zero emissions and net zero emissions is needed to halt further warming,” says Dr Oliver Geden who’s part of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and an expert in carbon capture.
“Capturing directly from seawater is one of the options. Directly capturing it from the air is another one. There are basically 15 to 20 options, and in the end the question of what to use, of course, will depend on the cost.”

The Seacure project has £3m of funding from the government and is one of 15 pilot projects being backed in the UK as part of efforts to develop technologies that capture and store greenhouse gases.
“Removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere is essential in helping us achieve net zero,” says energy minister Kerry McCarthy. “Innovative projects like SeaCURE at the University of Exeter play an important role in creating the green technologies needed to make this happen, while supporting skilled jobs and boosting growth.”
 University of Exeter
University of Exeter‘Some impact on environment’
There’s also the question of what a large quantity of low-carbon water would do to the sea and the things that live in it. In Weymouth it dribbles out of a pipe in such small quantities it is unlikely to have any impact.
Guy Hooper is a PhD student at Exeter University and is researching the possible impacts of the project. He’s been exposing marine creatures to low-carbon water under laboratory conditions.
“Marine organisms rely on carbon to do certain things,” he says. “So phytoplankton use carbon to photosynthesize while things like mussels also use carbon to build their shells.”
Hooper says early indications are that massively increasing the amount of low-carbon water could have some impact on the environment.
“It might be damaging but there might be ways to mitigate that – for example through pre-diluting the low-carbon water. It’s important this is included in the discussion early on.”