AFP
AFPAshish Chauhan dreams of pursuing an MBA at an American university next year – a goal he describes as being “stamped in his brain”.
The 29-year-old finance professional from India (whose name has been changed on request) hopes to eventually work in the US, but says he now feels conflicted amid an immigration row sparked by President-elect Donald Trump’s supporters over a long-standing US visa programme.
The H-1B visa programme, which brings skilled foreign workers to the US, faces criticism for undercutting American workers but is praised for attracting global talent. The president-elect, once a critic, now supports the 34-year-old programme, while tech billionaire Elon Musk defends it as key to securing top engineering talent.
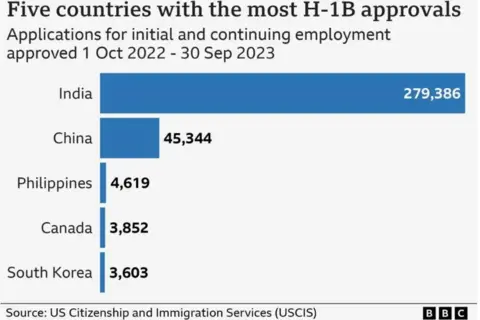
Indian nationals like Mr Chauhan dominate the programme, receiving 72% of H-1B visas, followed by 12% for Chinese citizens. The majority of H-1B visa holders worked in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, with 65% in computer-related jobs, in 2023. Their median annual salary was $118,000 (£94,000).
Concerns over H-1B visas tie into broader immigration debates.
A Pew Research report shows that US immigration rose by 1.6 million in 2023, the largest increase in more than 20 years. Immigrants now comprise over 14% of the population – the highest since 1910. Indians are the second-largest immigrant group – after Mexicans – in the US. Many Americans fear this surge in immigration could harm job prospects or hinder assimilation.
India has also surpassed China as the leading source of international students, with a record 331,602 Indian students in the US in 2023-2024, according to the latest Open Doors Report on International Educational Exchange. Most rely on loans, and any visa freeze could potentially devastate family finances.
“My worry is that this [resistance to H-1B visas] could also spark animosity towards the Indians living there. But I can’t park my ambitions, put my life on hold and wait for the volatility to subside because it’s been like this for years now,” Mr Chauhan says.
Efforts to restrict the H-1B programme peaked under Trump’s first term, when he signed a 2017 order increasing application scrutiny and fraud detection. Rejection rates soared to 24% in 2018, compared to 5-8% under President Barack Obama and 2-4% under President Joe Biden. The total number of approved H-1B applicants under Biden remained similar to Trump’s first term.
“The first Trump administration tightened H-1B visas by increasing denial rates and slowing processing times, making it harder for people to get visas in time. It is unclear whether that will happen again in the second Trump administration,” Stephen Yale-Loehr, an immigration scholar at Cornell Law School, told the BBC.
“Some people like Elon Musk want to preserve the H-1B visas, while other officials in the new administration want to restrict all immigration, including H-1Bs. It is too early to tell which side will prevail.”
Indians have a long relationship with the H-1B visa. The programme is also the reason for the “rise of Indian-Americans into the highest educated and highest earning group, immigrant or native in the US”, say the authors of The Other One Percent, a study on Indians in America.
US-based researchers Sanjoy Chakravorty, Devesh Kapur and Nirvikar Singh noted that new Indian immigrants spoke different languages and lived in different areas than earlier arrivals. Hindi, Tamil and Telugu speakers grew in number, and Indian-American communities shifted from New York and Michigan to larger clusters in California and New Jersey. The skilled visa programme helped create a “new map of Indian-Americans”.

The biggest draw of H-1B visas is the opportunity to earn significantly higher salaries, according to Mr Chauhan. The US offers higher pay, and for someone who is the first in their family to achieve professional qualifications, earning that much can be life-changing. “The fascination with H-1Bs is directly tied to the wage gap between India and the US for the same engineering roles,” he says.
But not everybody is happy with the programme. For many, the H-1B programme is an aspirational pathway for permanent residency or a US green card. While H-1B itself is a temporary work visa, it allows visa holders to live and work in the US for up to six years. During this time, many H-1B holders apply for a green card through employment-based immigration categories, typically sponsored by their employers. This takes time.
More than a million Indians, including dependents, are currently waiting in employment-based green card categories. “Getting a green card means signing up for an endless wait for 20-30 years,” says Atal Agarwal, who runs a firm in India that uses AI to help find visa options globally for education and jobs.
Mr Agarwal moved to the US after graduating in 2017 and worked at a software company for a few years. He says getting the H-1B visa was fairly straightforward, but then it seemed he had “reached a dead end”. He returned to India.
“It’s an unstable situation. Your employer has to sponsor you and since the pathway to a green card is so long, you are basically tied to them. If you lose your job, you only get 60 days to find a new one. Every person who is going on merit to the US should have a pathway to a green card within three to five years.”
This could be one reason that the visa programme has got tied up with immigration. “H-1B is a high-skilled, worker mobility visa. It is not an immigration visa. But it gets clubbed with immigration and illegal immigration and becomes a sensitive issue,” Shivendra Singh, vice president of global trade development at Nasscom, the Indian technology industry trade group, told the BBC.
Many in the US believe the H-1B visa programme is flawed. They cite widespread fraud and abuse, especially by major Indian IT firms which are top recipients of these visas. In October, a US court found Cognizant guilty of discriminating against over 2,000 non-Indian employees between 2013 and 2022, though the company plans to appeal. Last week, Farah Stockman of The New York Times wrote that “for more than a decade, Americans working in the tech industry have been systematically laid off and replaced by cheaper H-1B visa holders”.
Mr. Singh of Nasscom argues that H-1B visa workers are not underpaid, as employers must pay them above the prevailing or actual wage of comparable US workers in the area. Companies also invest tens of thousands of dollars in legal and government fees for these costly visas.
Also, it has not been a one-way traffic: Indian tech giants have hired and supported nearly 600,000 American workers and spent over a billion dollars on upskilling nearly three million students across 130 US colleges, according to Mr Singh. The Indian tech industry has prioritised US worker hiring and they bring employees on H-1B visas only when they are unable to find locals with the skills they need, he said.
India is working to ensure the H-1B visa programme remains secure as Trump prepares to take office later this month. “Our countries share a strong and growing economic and technological partnership, and the mobility of skilled professionals is a vital component of this relationship,” India’s foreign ministry spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal told journalists last week.
So what should students aspiring for jobs in the US do? “Any immigration changes in the US will take time to implement. Students should pick the best college for them, wherever that may be. With good immigration counsel, they will be able to figure out what to do,” says Mr Yale-Loehr.
For now, despite the political turbulence in the US, Indian interest in H-1B visas remains steadfast, with students resolute in pursuing the American dream.